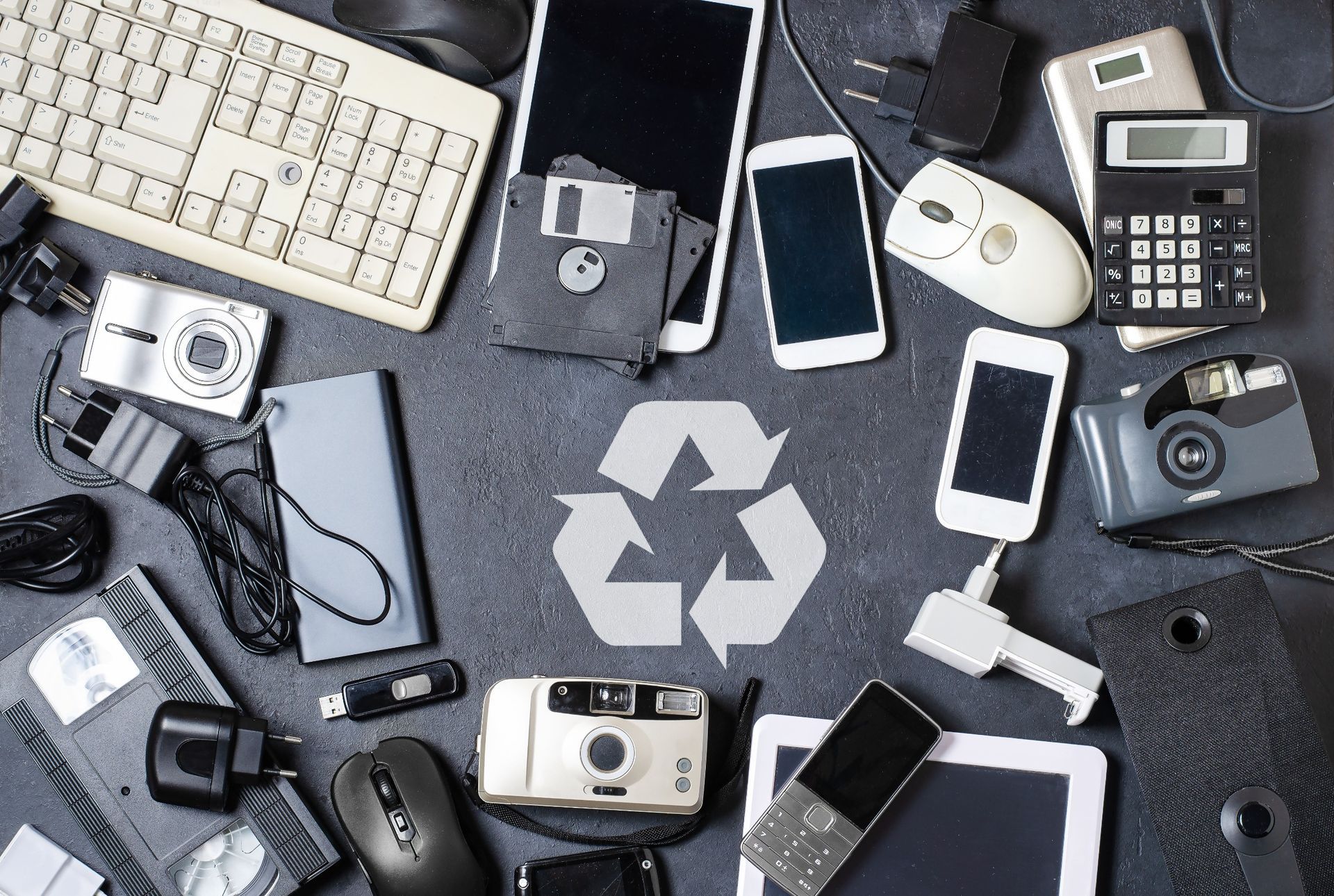
What Happens to Your Electronics After E-Waste Recycling?
What Happens to Your Electronics After E-Waste Recycling?
When your old smartphone, laptop, or tablet has reached the end of its life, recycling it might not be the first solution that comes to mind.
However, e-waste recycling is not only important for the environment but also a means to recover valuable materials and reduce hazardous waste in landfills. But have you ever wondered what really happens to your electronics after they are dropped off for recycling? From collection to final processing, this blog will break down the intricate steps of the e-waste recycling process.
Whether you’re searching for information on e-waste recycling in Massachusetts or want to know more about electronic waste disposal, this guide offers a peek behind the scenes of responsible recycling.
Why E-Waste Recycling Matters
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of what happens to your devices, it’s important to understand why e-waste recycling matters.
- Environmental Impact: Electronics contain toxic materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium that can leach into soil and water if left in landfills. Recycling prevents contamination and promotes a cleaner environment.
- Resource Recovery: Your old devices are filled with valuable materials like gold, silver, copper, and palladium. Recovering these metals reduces the need for environmentally damaging mining activities.
- Energy Savings: Recycling electronics often requires less energy compared to mining and refining new raw materials.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many states, including Massachusetts, have regulations to ensure proper electronic waste disposal and recycling.
Now that we understand the importance of recycling, let's explore what exactly happens to your old gadgets.
Step 1: Collection and Drop-off
The first step in the e-waste recycling process is collection. Electronics are gathered through various channels such as authorized recycling centers, community drop-off events, and retailer programs.
Some states, like Massachusetts, have dedicated facilities for e-waste recycling, where residents can responsibly dispose of their old devices. Many electronics brands and retailers also offer trade-in or take-back programs to make recycling more convenient. Once collected, the e-waste moves to a recycling facility for further processing.
Tip: Check Local Recycling Programs
If you’re a resident of Massachusetts, look for certified e-waste recycling centers in your area. Many facilities are designed to safely handle everything from cell phones to larger appliances.
Step 2: Sorting and Categorizing
At the recycling facility, electronic items are sorted and categorized by type. For example, computers, mobile phones, televisions, and batteries are often processed differently.
This manual or automated sorting process ensures that specific components are directed toward the appropriate recycling streams. Devices containing hazardous materials are separated early on to prevent potential contamination during processing.
Common E-Waste Categories:
- Large household electronics: TVs, monitors, and refrigerators.
- Small devices: Smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches.
- Peripheral equipment: Keyboards, mice, and chargers.
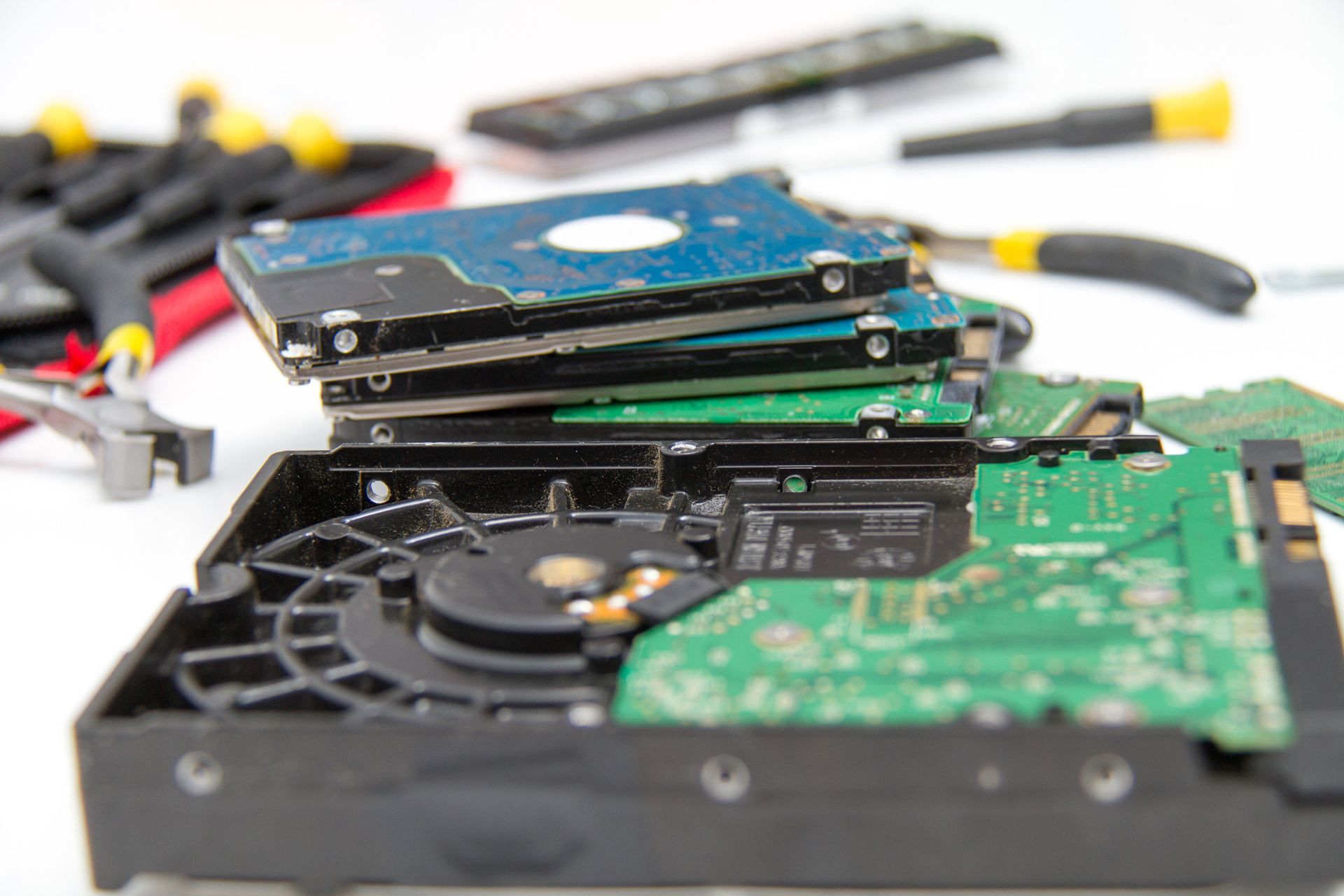
Step 3: Dismantling
After sorting, electronics are dismantled. Skilled technicians or automated machines remove components from the devices. This step is particularly important for recovering materials that can be reused or recycled.
Key Parts Removed During Dismantling Include:
- Batteries: Batteries are often removed first as they require specialized handling due to chemical risks.
- Circuit Boards: Circuit boards contain precious metals and are sent for further extraction.
- Glass and Plastics: Screens and casings are separated for recycling or repurposing.
What Happens to Each Component?
- Batteries are processed separately to recover metals like lithium and cobalt.
- Circuit boards undergo roasting or chemical extraction to recover gold, copper, and silver.
- Plastics might be shredded and reused to create new consumer goods.
Step 4: Shredding and Separation
With the devices dismantled, the next step is shredding. Shredders break down larger components into smaller pieces, making it easier to separate individual materials.
Advanced separation technologies might then be used, including magnetic, eddy current, and optical systems, to sort materials like metals, plastics, and glass.
- Magnetic Separation: Extracts ferrous metals like steel from the shred.
- Non-Magnetic Separation: Materials like aluminum and copper are pulled apart using eddy currents or density control systems.
- Optical Separation: Scanners help identify and sort high-quality plastics.
This stage ensures that everything is as efficiently divided as possible, with minimal contamination.
Step 5: Material Recovery
Now comes the rewarding part—recovering valuable materials. Precious metals like gold, silver, and palladium are extracted and refined. These recovered materials can then re-enter the production cycle to manufacture new electronics or other products.
For example, Apple’s recent "Liam" and "Daisy" robots are designed specifically to recover rare materials from their devices and reuse them in their production. Other companies are following suit to promote sustainability and reduce their environmental footprint.
Recovered materials might be used for various purposes, such as:
- Manufacturing new consumer electronics.
- Producing wiring for infrastructure projects.
- Crafting jewelry or other luxury goods.
Step 6: Proper Disposal of Residual Materials
Unfortunately, not every bit of e-waste can be effectively recycled. Certain hazardous materials or low-value plastics might be left over at the end of the process.
However, these remaining materials undergo environmentally sound disposal methods, ensuring they don't harm the earth. Certified facilities follow strict guidelines to prevent contamination.
Example in Massachusetts
Organizations certified by e-Stewards and R2 ensure that all residual waste is handled responsibly. This aligns with the state’s progressive efforts toward safe electronic waste disposal.
Challenges in the E-Waste Recycling Landscape
Despite all the benefits, e-waste recycling isn’t without its challenges.
- Low Recycling Rates: Only 17.4% of global e-waste was officially recycled in recent years, according to the UN Global E-Waste Monitor.
- Complex Devices: Modern electronics are made with intricate designs, making dismantling and recovery more challenging.
- Lack of Awareness: Many consumers are still unaware of proper e-waste recycling practices and outlets in their area.
How You Can Make a Difference
E-waste recycling isn’t just the responsibility of large organizations or governments—it starts with individual action.
- Recycle Responsibly: Drop your used electronics at certified recycling centers or authorized retailer programs.
- Buy Sustainable: Choose products with eco-friendly certifications or brands that prioritize sustainable practices.
- Spread Awareness: Educate friends and family about the importance of electronic waste disposal.
Take the Next Step in Responsible Recycling
Understanding what happens to your electronics after e-waste recycling gives you a clearer picture of its benefits. By participating in e-waste recycling, you can contribute to a cleaner planet, conserve resources, and reduce harmful waste.
If you're in Massachusetts, search for certified e-waste recycling Massachusetts centers to get started. Drop off your old electronics today and be part of the responsible recycling movement!
Ready to recycle your e-waste?
Do you have old devices lying around? Don’t wait for them to gather dust. At Data Shredder Corporation in Massachusetts, we understand how crucial it is to destroy sensitive data securely and recycle e-waste.
We provide top-notch hard drive data destruction, hard drive shredding, and recycling services in Massachusetts, ensuring your peace of mind while benefiting the planet's health. We also provide top-notch hardware asset management services.
Your trust is our top priority, and we're dedicated to safeguarding your information with our certified, dependable solutions. Before a security breach even whispers your name, give us a call at(508) 978-5198 or fill out our
contact form.

Contact Us
40 School Street, 2nd Floor
Framingham, MA 01701
Email: service@datashredder.net
Business Hours
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Sat - Sun
- Closed








Share On: